English blooms taxonomy assessment pdf
Title: Microsoft Word – Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measureable Verbs.docx Author: Smith, Sherri (English) Created Date: 11/1/2011 6:44:16 PM
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s verbs–also know as power verbs or thinking verbs–are extraordinarily powerful instructional planning tools. In fact, next to the concept of backward-design and power standards, they are likely the most useful tool a teacher-as-learning-designer has access to.
The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, often called Bloom’s Taxonomy, is a classification of the different objectives and skills that educators set for students. The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago.
Your English language learners should be developing thinking skills as they acquire English. Dust off your copy of Bloom’s Taxonomy and ask questions from all levels.
This is an assessment template which incorporates and implements Blooms Taxonomy to assess pupil understanding of topics and their application of higher order thinking skills using the 6 stages of Blooms Taxonomy.
‘Learning Outcomes and Level Descriptions’ Wednesday 23rd October 2013, 12.30-2.00pm . Tony Turjansky. Head of Academic Quality & University Learning and Teaching Fellow. Session aims • To define the relationships between: – National reference points (generic qualification and level descriptors and subject benchmark statements) and the writing of programme aims and learning outcomes
Questions at this level of Bloom’s taxonomy can be modified so that the langue is simplified but the task remains the same. English language learners can learn to give opinions, make judgments about the action in a story and evaluate the work of an author.
Bloom’s Taxonomy – Cognitive Levels Sample Verbs. Analysis Breaking down information into parts, or examining (and trying to understand the organizational structure of) information. Use words and phrases such as: what are the differences, analyze, explain, compare, separate, classify, arrange, etc., to encourage students to break information down into parts. Break down Characterize Classify
Congratulations and thank you so much for sharing with all of us this most valuable article, Bloom’s Taxonomy and its Use in Classroom Assessment.
This is an assessment template which incorporates and implements Blooms Taxonomy to assess pupil understanding of topics and their application of higher order thinking skills using the 6 stages of Blooms Taxonomy. As it is only a template it ca…
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items – Assessment ‹ Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items – Course Organization/Design up Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items – A Framework for Developing Online Assessment Items › Author(s): Draga Vidakovic, Jean Bevis, and Margo Alexander. In developing a WebCT based Precalculus course, we …
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Assessments Video & Lesson

Bloom’s Taxonomy (pdf) Cloud County Community College
5/09/2008 · An overview of assessment and an introduction to Bloom’s Taxonomy and it’s application to learning.
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a list of cognitive skills that is used by teachers to determine the level of thinking their students have achieved. The taxonomy ranks the cognitive skills on a continuum from
assessment. DRAFTING LEARNING OUTCOME STATEMENTS . When crafting student learning outcomes, it can be useful to consult a learning taxonomy to identify the kinds of learning you would like to foster in your course. Bloom’s Taxonomy—developed by educational theorist Benjamin Bloom in the 1950s and revised by Krathwohl et al. in 2001—identifies three domains of learning: cognitive
A STUDY OF STUDENTS COGNITIVE LEVELS USING BLOOMS TAXONOMY IN SOCIAL STUDIES Robert McBain Publication Date Sept 2011 ABSTRACT This was a simple classroom research project and its purpose was to examine how high up in the scale of Blooms taxonomy students were able reach to to understand higher order thinking skills when studying critical thinking questions. Two …
Blooms Taxonomy– Application in Exam Papers Assessment S. Ilango Sivaraman1 and Dinesh Krishna2 1,2Caledonian College of Engineering, Muscat, Oman Abstract– Testing the students’ cognitive level is the prime objective of any assessment system. However, it is perhaps necessary to review and introduce steps in the examination paper design to ensure that the student is tested for the
11/1/2017 Teaching English Grammar using Bloom’s Revised TaxonomySlideShare…
Bloom’s Taxonomy. This taxonomy was originally created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 to categorize a continuum of educational objectives. These objectives are described in terms of student-centered actions that represent the kind of knowledge and intellectual engagement we want our students to …

English language learners should be asked critical thinking questions from all levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Some of the tasks on the taxonomy are difficult for ELLs because they lack the language and vocabulary to work in English. However, teachers need to ask questions from all levels of the taxonomy that are age appropriate and at the English language level of the English language …
Summary of How Evaluation, Assessment, Measurement and Testing Terms Are Related 4 Course Learning Objectives 5 Abilities and Behaviors Related to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives 6 Illustrative Action Verbs for Defining Objectives using Bloom’s Taxonomy 7 Examples of Instructional Objectives for the Cognitive Domain 8 Resources on Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain …
Bloom (1956) has provided us with his taxonomy to assist us to compose questions on different levels of thinking. This taxonomy ranges from lower to higher levels of cognitive thinking. These levels are (I will shortly provide more detail of each level):
3. the 1 the taxonomy table the cognitive process dimension create remember understand apply analyze evaluate knowledge dimens10n factual knowledge
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide of assessment activities. This part of the document provides a guide for developing assessment activities based on the key active verbs in the Australian Curriculum: Digital Technologies using Bloom’s Taxonomy as a framework.
The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable tool that could enable analysis and discussion of programming assessment if it could be interpreted consistently. We discuss each of the Bloom classification categories and provide a consistent interpretation with concrete exemplars that will allow computer science educators to utilise Bloom’s Taxonomy for programming assessment. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy …
What level from Bloom’s taxonomy is being assessed: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and/or evaluation. Is the level appropriate given the objectives for the course/unit/lesson? • Is the assessment at a level appropriate to the level of the course (first year, graduate etc.)? • How well does the content of the assessment match the objectives being assessed

PDF Bloom’s Taxonomy is difficult to apply consistently to assessment tasks in introductory programming courses. The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable …
An excellent resource linking Bloom’s Taxonomy to specific questions/tasks in English.
• knowledge of major ideas • mastery of subject matter • list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, name, who, when, where, etc. Comprehension
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy: Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy assessment taxonomy 46 We argue that, both in mathematics and in mathematical literacy, the processes of problem-posing and problem-solving require reasoning in a range of ways – in asking the right questions, in choosing the mathematical tools that might assist in answering them, in …
blooms made easy: aligning nqf levels with appropriate teaching, learning and assessment practices m maree (tlu, may 2016) nqf level blooms taxonomy teaching and learning assessment
Blooms Taxonomy Questions Assessment For Learning Strategies Teaching Resources Differentiation Strategies Teaching Activities Teaching Tools Learning Objectives Teaching Methods Formative Assessment. Blooms Taxonomy Questions: Designed for a key ring, this resource would be great to have for small group work when talking about Bloom’s. Bloom’s taxonomy is essential when talking …
Bloom’s taxonomy and English language learners
– harry potter and the deathly hallows hpmedia bloomsbury extract pdf
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
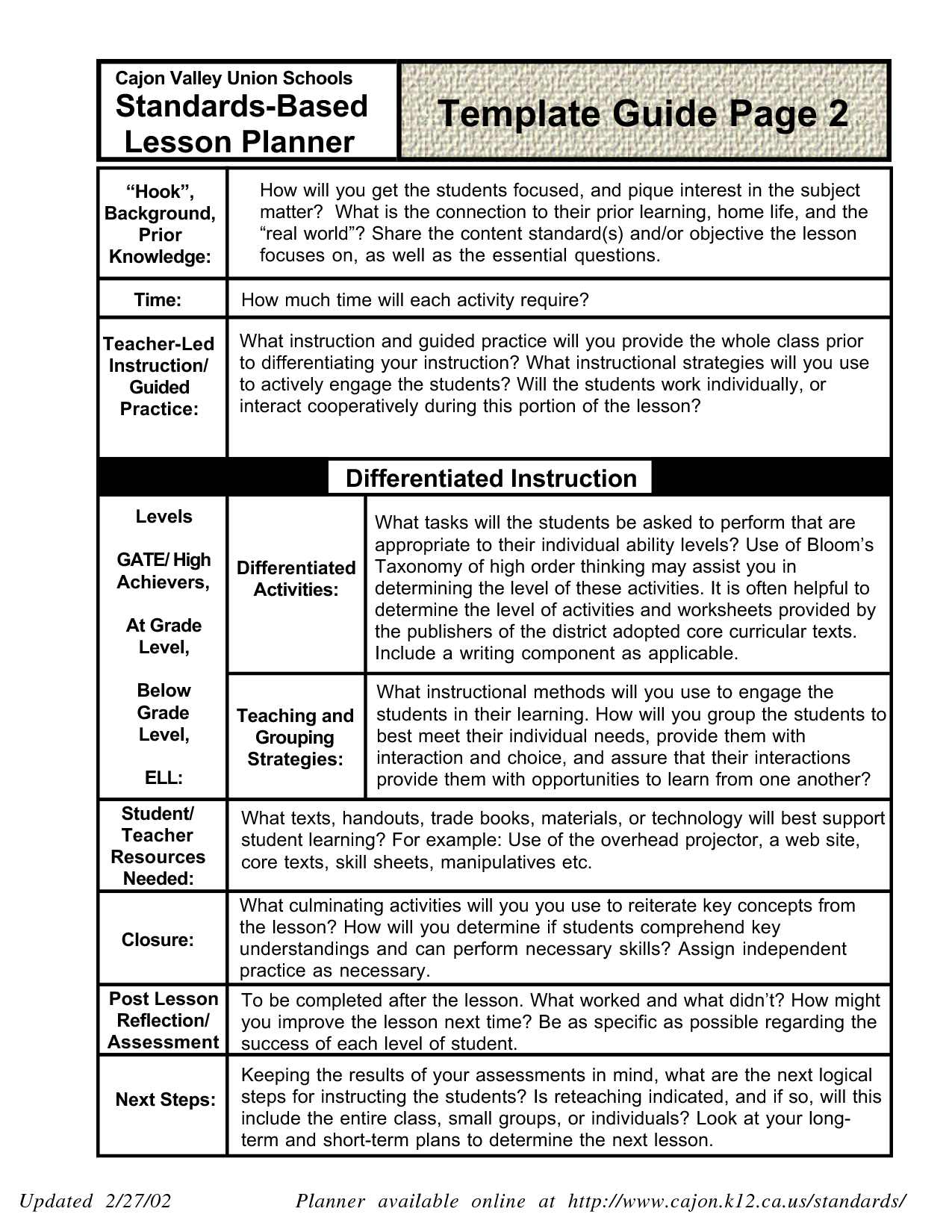
Blooms Taxonomy Verbs Blooms/Marzano’s Taxonomy
Teaching English Grammar Using Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy

Observation of Learning Teaching and Assessment 2012-13
Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Clark College

Graduate Outcomes Teaching/Assessment NQF Level Theory
Intro To Assessment and Bloom YouTube
– All Ages Bloom’s Taxonomy – eriding.net
Blooms Taxonomy Digital Technologies Hub

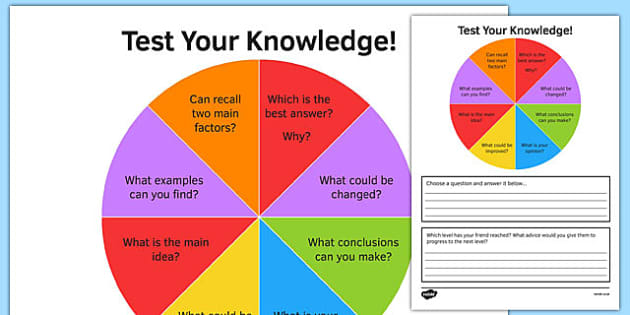
Bloom’s Taxonomy in English by rec208 TES Resources
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items
Bloom’s Taxonomy and English Language Learners Teaching
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable tool that could enable analysis and discussion of programming assessment if it could be interpreted consistently. We discuss each of the Bloom classification categories and provide a consistent interpretation with concrete exemplars that will allow computer science educators to utilise Bloom’s Taxonomy for programming assessment. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy …
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s verbs–also know as power verbs or thinking verbs–are extraordinarily powerful instructional planning tools. In fact, next to the concept of backward-design and power standards, they are likely the most useful tool a teacher-as-learning-designer has access to.
Blooms Taxonomy– Application in Exam Papers Assessment S. Ilango Sivaraman1 and Dinesh Krishna2 1,2Caledonian College of Engineering, Muscat, Oman Abstract– Testing the students’ cognitive level is the prime objective of any assessment system. However, it is perhaps necessary to review and introduce steps in the examination paper design to ensure that the student is tested for the
A STUDY OF STUDENTS COGNITIVE LEVELS USING BLOOMS TAXONOMY IN SOCIAL STUDIES Robert McBain Publication Date Sept 2011 ABSTRACT This was a simple classroom research project and its purpose was to examine how high up in the scale of Blooms taxonomy students were able reach to to understand higher order thinking skills when studying critical thinking questions. Two …
Blooms Taxonomy Questions Assessment For Learning Strategies Teaching Resources Differentiation Strategies Teaching Activities Teaching Tools Learning Objectives Teaching Methods Formative Assessment. Blooms Taxonomy Questions: Designed for a key ring, this resource would be great to have for small group work when talking about Bloom’s. Bloom’s taxonomy is essential when talking …
‘Learning Outcomes and Level Descriptions’ Wednesday 23rd October 2013, 12.30-2.00pm . Tony Turjansky. Head of Academic Quality & University Learning and Teaching Fellow. Session aims • To define the relationships between: – National reference points (generic qualification and level descriptors and subject benchmark statements) and the writing of programme aims and learning outcomes
11/1/2017 Teaching English Grammar using Bloom’s Revised TaxonomySlideShare…
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy: Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy assessment taxonomy 46 We argue that, both in mathematics and in mathematical literacy, the processes of problem-posing and problem-solving require reasoning in a range of ways – in asking the right questions, in choosing the mathematical tools that might assist in answering them, in …
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Clark College
Blooms Taxonomy– Application in Exam Papers Assessment S. Ilango Sivaraman1 and Dinesh Krishna2 1,2Caledonian College of Engineering, Muscat, Oman Abstract– Testing the students’ cognitive level is the prime objective of any assessment system. However, it is perhaps necessary to review and introduce steps in the examination paper design to ensure that the student is tested for the
PDF Bloom’s Taxonomy is difficult to apply consistently to assessment tasks in introductory programming courses. The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable …
• knowledge of major ideas • mastery of subject matter • list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, name, who, when, where, etc. Comprehension
3. the 1 the taxonomy table the cognitive process dimension create remember understand apply analyze evaluate knowledge dimens10n factual knowledge
A STUDY OF STUDENTS COGNITIVE LEVELS USING BLOOMS TAXONOMY IN SOCIAL STUDIES Robert McBain Publication Date Sept 2011 ABSTRACT This was a simple classroom research project and its purpose was to examine how high up in the scale of Blooms taxonomy students were able reach to to understand higher order thinking skills when studying critical thinking questions. Two …
Summary of How Evaluation, Assessment, Measurement and Testing Terms Are Related 4 Course Learning Objectives 5 Abilities and Behaviors Related to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives 6 Illustrative Action Verbs for Defining Objectives using Bloom’s Taxonomy 7 Examples of Instructional Objectives for the Cognitive Domain 8 Resources on Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain …
This is an assessment template which incorporates and implements Blooms Taxonomy to assess pupil understanding of topics and their application of higher order thinking skills using the 6 stages of Blooms Taxonomy. As it is only a template it ca…
English language learners should be asked critical thinking questions from all levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Some of the tasks on the taxonomy are difficult for ELLs because they lack the language and vocabulary to work in English. However, teachers need to ask questions from all levels of the taxonomy that are age appropriate and at the English language level of the English language …
An excellent resource linking Bloom’s Taxonomy to specific questions/tasks in English.
What level from Bloom’s taxonomy is being assessed: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and/or evaluation. Is the level appropriate given the objectives for the course/unit/lesson? • Is the assessment at a level appropriate to the level of the course (first year, graduate etc.)? • How well does the content of the assessment match the objectives being assessed
blooms made easy: aligning nqf levels with appropriate teaching, learning and assessment practices m maree (tlu, may 2016) nqf level blooms taxonomy teaching and learning assessment
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide of assessment activities. This part of the document provides a guide for developing assessment activities based on the key active verbs in the Australian Curriculum: Digital Technologies using Bloom’s Taxonomy as a framework.
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items – Assessment ‹ Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items – Course Organization/Design up Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items – A Framework for Developing Online Assessment Items › Author(s): Draga Vidakovic, Jean Bevis, and Margo Alexander. In developing a WebCT based Precalculus course, we …
All Ages Bloom’s Taxonomy – eriding.net
Blooms Taxonomy Verbs Blooms/Marzano’s Taxonomy
Your English language learners should be developing thinking skills as they acquire English. Dust off your copy of Bloom’s Taxonomy and ask questions from all levels.
Summary of How Evaluation, Assessment, Measurement and Testing Terms Are Related 4 Course Learning Objectives 5 Abilities and Behaviors Related to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives 6 Illustrative Action Verbs for Defining Objectives using Bloom’s Taxonomy 7 Examples of Instructional Objectives for the Cognitive Domain 8 Resources on Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain …
This is an assessment template which incorporates and implements Blooms Taxonomy to assess pupil understanding of topics and their application of higher order thinking skills using the 6 stages of Blooms Taxonomy. As it is only a template it ca…
Title: Microsoft Word – Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measureable Verbs.docx Author: Smith, Sherri (English) Created Date: 11/1/2011 6:44:16 PM
assessment. DRAFTING LEARNING OUTCOME STATEMENTS . When crafting student learning outcomes, it can be useful to consult a learning taxonomy to identify the kinds of learning you would like to foster in your course. Bloom’s Taxonomy—developed by educational theorist Benjamin Bloom in the 1950s and revised by Krathwohl et al. in 2001—identifies three domains of learning: cognitive
English language learners should be asked critical thinking questions from all levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Some of the tasks on the taxonomy are difficult for ELLs because they lack the language and vocabulary to work in English. However, teachers need to ask questions from all levels of the taxonomy that are age appropriate and at the English language level of the English language …
11/1/2017 Teaching English Grammar using Bloom’s Revised TaxonomySlideShare…
The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable tool that could enable analysis and discussion of programming assessment if it could be interpreted consistently. We discuss each of the Bloom classification categories and provide a consistent interpretation with concrete exemplars that will allow computer science educators to utilise Bloom’s Taxonomy for programming assessment. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy …
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a list of cognitive skills that is used by teachers to determine the level of thinking their students have achieved. The taxonomy ranks the cognitive skills on a continuum from
A STUDY OF STUDENTS COGNITIVE LEVELS USING BLOOMS TAXONOMY IN SOCIAL STUDIES Robert McBain Publication Date Sept 2011 ABSTRACT This was a simple classroom research project and its purpose was to examine how high up in the scale of Blooms taxonomy students were able reach to to understand higher order thinking skills when studying critical thinking questions. Two …
• knowledge of major ideas • mastery of subject matter • list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, name, who, when, where, etc. Comprehension
PDF Bloom’s Taxonomy is difficult to apply consistently to assessment tasks in introductory programming courses. The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable …
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Assessments Video & Lesson
Bloom’s taxonomy and English language learners
This is an assessment template which incorporates and implements Blooms Taxonomy to assess pupil understanding of topics and their application of higher order thinking skills using the 6 stages of Blooms Taxonomy.
Bloom’s Taxonomy – Cognitive Levels Sample Verbs. Analysis Breaking down information into parts, or examining (and trying to understand the organizational structure of) information. Use words and phrases such as: what are the differences, analyze, explain, compare, separate, classify, arrange, etc., to encourage students to break information down into parts. Break down Characterize Classify
5/09/2008 · An overview of assessment and an introduction to Bloom’s Taxonomy and it’s application to learning.
Title: Microsoft Word – Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measureable Verbs.docx Author: Smith, Sherri (English) Created Date: 11/1/2011 6:44:16 PM
English language learners should be asked critical thinking questions from all levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Some of the tasks on the taxonomy are difficult for ELLs because they lack the language and vocabulary to work in English. However, teachers need to ask questions from all levels of the taxonomy that are age appropriate and at the English language level of the English language …
‘Learning Outcomes and Level Descriptions’ Wednesday 23rd October 2013, 12.30-2.00pm . Tony Turjansky. Head of Academic Quality & University Learning and Teaching Fellow. Session aims • To define the relationships between: – National reference points (generic qualification and level descriptors and subject benchmark statements) and the writing of programme aims and learning outcomes
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a list of cognitive skills that is used by teachers to determine the level of thinking their students have achieved. The taxonomy ranks the cognitive skills on a continuum from
Bloom’s Taxonomy. This taxonomy was originally created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 to categorize a continuum of educational objectives. These objectives are described in terms of student-centered actions that represent the kind of knowledge and intellectual engagement we want our students to …
Blooms Taxonomy– Application in Exam Papers Assessment S. Ilango Sivaraman1 and Dinesh Krishna2 1,2Caledonian College of Engineering, Muscat, Oman Abstract– Testing the students’ cognitive level is the prime objective of any assessment system. However, it is perhaps necessary to review and introduce steps in the examination paper design to ensure that the student is tested for the
Bloom (1956) has provided us with his taxonomy to assist us to compose questions on different levels of thinking. This taxonomy ranges from lower to higher levels of cognitive thinking. These levels are (I will shortly provide more detail of each level):
An excellent resource linking Bloom’s Taxonomy to specific questions/tasks in English.
A STUDY OF STUDENTS COGNITIVE LEVELS USING BLOOMS TAXONOMY IN SOCIAL STUDIES Robert McBain Publication Date Sept 2011 ABSTRACT This was a simple classroom research project and its purpose was to examine how high up in the scale of Blooms taxonomy students were able reach to to understand higher order thinking skills when studying critical thinking questions. Two …
11/1/2017 Teaching English Grammar using Bloom’s Revised TaxonomySlideShare…
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide of assessment activities. This part of the document provides a guide for developing assessment activities based on the key active verbs in the Australian Curriculum: Digital Technologies using Bloom’s Taxonomy as a framework.
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy: Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy assessment taxonomy 46 We argue that, both in mathematics and in mathematical literacy, the processes of problem-posing and problem-solving require reasoning in a range of ways – in asking the right questions, in choosing the mathematical tools that might assist in answering them, in …

Elijah
• knowledge of major ideas • mastery of subject matter • list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, name, who, when, where, etc. Comprehension
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items
Blooms Taxonomy Verbs Blooms/Marzano’s Taxonomy
Christopher
Summary of How Evaluation, Assessment, Measurement and Testing Terms Are Related 4 Course Learning Objectives 5 Abilities and Behaviors Related to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives 6 Illustrative Action Verbs for Defining Objectives using Bloom’s Taxonomy 7 Examples of Instructional Objectives for the Cognitive Domain 8 Resources on Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain …
All Ages Bloom’s Taxonomy – eriding.net
Blooms Taxonomy Assessment and Evaluation Tool by
Logan
Summary of How Evaluation, Assessment, Measurement and Testing Terms Are Related 4 Course Learning Objectives 5 Abilities and Behaviors Related to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives 6 Illustrative Action Verbs for Defining Objectives using Bloom’s Taxonomy 7 Examples of Instructional Objectives for the Cognitive Domain 8 Resources on Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain …
Blooms Taxonomy Assessment and Evaluation Tool by
Abigail
This is an assessment template which incorporates and implements Blooms Taxonomy to assess pupil understanding of topics and their application of higher order thinking skills using the 6 stages of Blooms Taxonomy. As it is only a template it ca…
Bloom’s Taxonomy with Corresponding Verbs
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measureable Verbs marshall.edu
Alexis
3. the 1 the taxonomy table the cognitive process dimension create remember understand apply analyze evaluate knowledge dimens10n factual knowledge
Intro To Assessment and Bloom YouTube
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
Owen
Questions at this level of Bloom’s taxonomy can be modified so that the langue is simplified but the task remains the same. English language learners can learn to give opinions, make judgments about the action in a story and evaluate the work of an author.
Blooms Taxonomy Assessment and Evaluation Tool by
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
Teaching English Grammar Using Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy
Ian
Bloom’s Taxonomy – Cognitive Levels Sample Verbs. Analysis Breaking down information into parts, or examining (and trying to understand the organizational structure of) information. Use words and phrases such as: what are the differences, analyze, explain, compare, separate, classify, arrange, etc., to encourage students to break information down into parts. Break down Characterize Classify
Bloom’s Taxonomy (pdf) Cloud County Community College
(PDF) Bloom’s taxonomy for CS assessment ResearchGate
Blooms Taxonomy Verbs Blooms/Marzano’s Taxonomy
Elizabeth
Bloom (1956) has provided us with his taxonomy to assist us to compose questions on different levels of thinking. This taxonomy ranges from lower to higher levels of cognitive thinking. These levels are (I will shortly provide more detail of each level):
Intro To Assessment and Bloom YouTube
Isabella
Bloom’s Taxonomy – Cognitive Levels Sample Verbs. Analysis Breaking down information into parts, or examining (and trying to understand the organizational structure of) information. Use words and phrases such as: what are the differences, analyze, explain, compare, separate, classify, arrange, etc., to encourage students to break information down into parts. Break down Characterize Classify
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy
Ryan
The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, often called Bloom’s Taxonomy, is a classification of the different objectives and skills that educators set for students. The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago.
(PDF) Bloom’s taxonomy for CS assessment ResearchGate
Evan
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a list of cognitive skills that is used by teachers to determine the level of thinking their students have achieved. The taxonomy ranks the cognitive skills on a continuum from
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measureable Verbs marshall.edu
Bloom’s Taxonomy and English Language Learners Teaching
(PDF) Bloom’s taxonomy for CS assessment ResearchGate
Alex
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy: Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy assessment taxonomy 46 We argue that, both in mathematics and in mathematical literacy, the processes of problem-posing and problem-solving require reasoning in a range of ways – in asking the right questions, in choosing the mathematical tools that might assist in answering them, in …
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
Bloom’s Taxonomy (pdf) Cloud County Community College
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items
Jack
Bloom’s Taxonomy – Cognitive Levels Sample Verbs. Analysis Breaking down information into parts, or examining (and trying to understand the organizational structure of) information. Use words and phrases such as: what are the differences, analyze, explain, compare, separate, classify, arrange, etc., to encourage students to break information down into parts. Break down Characterize Classify
Bloom’s Taxonomy and English Language Learners Teaching
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
Charles
3. the 1 the taxonomy table the cognitive process dimension create remember understand apply analyze evaluate knowledge dimens10n factual knowledge
Blooms Taxonomy Digital Technologies Hub
Teaching English Grammar Using Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy
Blooms Taxonomy Assessment and Evaluation Tool by
Ian
Bloom (1956) has provided us with his taxonomy to assist us to compose questions on different levels of thinking. This taxonomy ranges from lower to higher levels of cognitive thinking. These levels are (I will shortly provide more detail of each level):
(PDF) Bloom’s taxonomy for CS assessment ResearchGate
Adam
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s verbs–also know as power verbs or thinking verbs–are extraordinarily powerful instructional planning tools. In fact, next to the concept of backward-design and power standards, they are likely the most useful tool a teacher-as-learning-designer has access to.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Cognitive Levels
Aidan
Blooms Taxonomy Questions Assessment For Learning Strategies Teaching Resources Differentiation Strategies Teaching Activities Teaching Tools Learning Objectives Teaching Methods Formative Assessment. Blooms Taxonomy Questions: Designed for a key ring, this resource would be great to have for small group work when talking about Bloom’s. Bloom’s taxonomy is essential when talking …
All Ages Bloom’s Taxonomy – eriding.net
Bloom’s Taxonomy with Corresponding Verbs
Kylie
The Bloom taxonomy is a valuable tool that could enable analysis and discussion of programming assessment if it could be interpreted consistently. We discuss each of the Bloom classification categories and provide a consistent interpretation with concrete exemplars that will allow computer science educators to utilise Bloom’s Taxonomy for programming assessment. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy …
Critiquing the Mathematical Literacy Assessment Taxonomy
All Ages Bloom’s Taxonomy – eriding.net
Lucas
Blooms Taxonomy– Application in Exam Papers Assessment S. Ilango Sivaraman1 and Dinesh Krishna2 1,2Caledonian College of Engineering, Muscat, Oman Abstract– Testing the students’ cognitive level is the prime objective of any assessment system. However, it is perhaps necessary to review and introduce steps in the examination paper design to ensure that the student is tested for the
‘Learning Outcomes and Level Descriptions’ Wednesday 23rd
Sara
What level from Bloom’s taxonomy is being assessed: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and/or evaluation. Is the level appropriate given the objectives for the course/unit/lesson? • Is the assessment at a level appropriate to the level of the course (first year, graduate etc.)? • How well does the content of the assessment match the objectives being assessed
Blooms Taxonomy Verbs Blooms/Marzano’s Taxonomy
Teaching English Grammar Using Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Eberly Center – Carnegie Mellon University
Daniel
The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, often called Bloom’s Taxonomy, is a classification of the different objectives and skills that educators set for students. The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago.
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items
Bloom’s Taxonomy and English Language Learners Teaching
Blooms Taxonomy Digital Technologies Hub
Trinity
A STUDY OF STUDENTS COGNITIVE LEVELS USING BLOOMS TAXONOMY IN SOCIAL STUDIES Robert McBain Publication Date Sept 2011 ABSTRACT This was a simple classroom research project and its purpose was to examine how high up in the scale of Blooms taxonomy students were able reach to to understand higher order thinking skills when studying critical thinking questions. Two …
Bloom’s Taxonomy in Developing Assessment Items
3. THE 1 THE TAXONOMY TABLE THE COGNITIVE PROCESS
Mary
5/09/2008 · An overview of assessment and an introduction to Bloom’s Taxonomy and it’s application to learning.
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Assessments Video & Lesson