Questions using bloom’s revised taxonomy in class pdf
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy/Essential Questions and Learning Maps (Click on the title above to see a chart with examples) Modified From: Anderson, Lorin W., and Krathwohl, David R. Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing.
Blooms Taxonomy and Differentiation in the Classroom Carol Ann Tomlinson and Benjamin Bloom’s research work in tandem to support brain research and learning. Tomlinson says that teachers can differentiate instruction based on student readiness, interests or learning profile.
“Bloom’s Question Prompts – This worksheet provides examples of questions that could be asked of students regarding texts that they have read at the various levels of Blooms Taxonomy.” “Bloom’s Question Prompts–good for planning and hanging on the literacy wall to use when doing read alouds.”
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions Knowledge Useful Verbs Sample Question Stems tell list describe relate locate write find state name
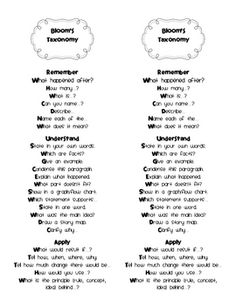
QUESTIONS FOR THE REVISED BLOOM’S TAXONOMY (from Quick Flip Questions for the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy EDUPRESS EP 729 – www.edupressinc.com ) LEVEL 1 – REMEMBERING LEVEL 2 – UNDERSTANDING LEVEL 3 – APPLYING Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas …
This revised Bloom’s taxonomy proves to be a very useful tool that can be used in all classrooms for several reasons listed below. About ninety percent of the questions students handle in any class are memory questions. The memory level is perfectly respectable and even essential in many learning situations. There are, however, disadvantages in using pure memory that an instructor should
With Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six levels of skills ranked in order from the most basic to the most complex. Each level of skill is associated with a verb, as learning is an action. Each level of skill is associated with a verb, as learning is an action.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Bloom’s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing performance tasks, crafting questions for conferring with students, and providing feedback on student work This resource is divided into different levels each with Keywords that exemplify
Bloom’s Taxonomy refers to a hierarchy ofquestion stemsthat teachers use to guide their students through the learning process.When students are initially introduced to a new topic, teachers should use Bloom’s to construct basic questions that ask students to recall simple facts from the material.
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy Various researchers have summarized how to use Bloom’s Taxonomy. Following are four interpretations that you can use as guides in helping
There is a quick flip book available on Amazon.com called Quick Flip Questions for Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy that is really helpful when planning lessons to include differentiation questions using Blooms Taxonomy.
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy: This document shows how to use a modernized style of the taxonomy in the classroom. K12 Blueprint: This is an extensive list of resources and applications for Bloom’s Taxonomy using Windows 8.
The taxonomy is a supplementary component to the critical thinking domain (one of the types of communication in the classroom). 3 Basic Levels of the Revised Taxonomy Questions The basic level of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Knowledge) is now called “Remembering.”
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions

Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Revised Bloom’s taxonomy (RBT) The idea that the original Bloom’s taxonomy was “ahead of its time” may be true in the 1960s, but in today’s educational climate it is very necessary.
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy [2] accounts for many of the traditional classroom practices, behaviours and actions but does not account for the new processes and actions associated with web 2.0 technologies and increasing ubiquitous computing.
Bloom’s Taxonomy categorizes levels of questions. Explore the taxonomy and find ways to implement each level in lesson plans and tests in your classroom. Explore the taxonomy and find ways to implement each level in lesson plans and tests in your classroom.
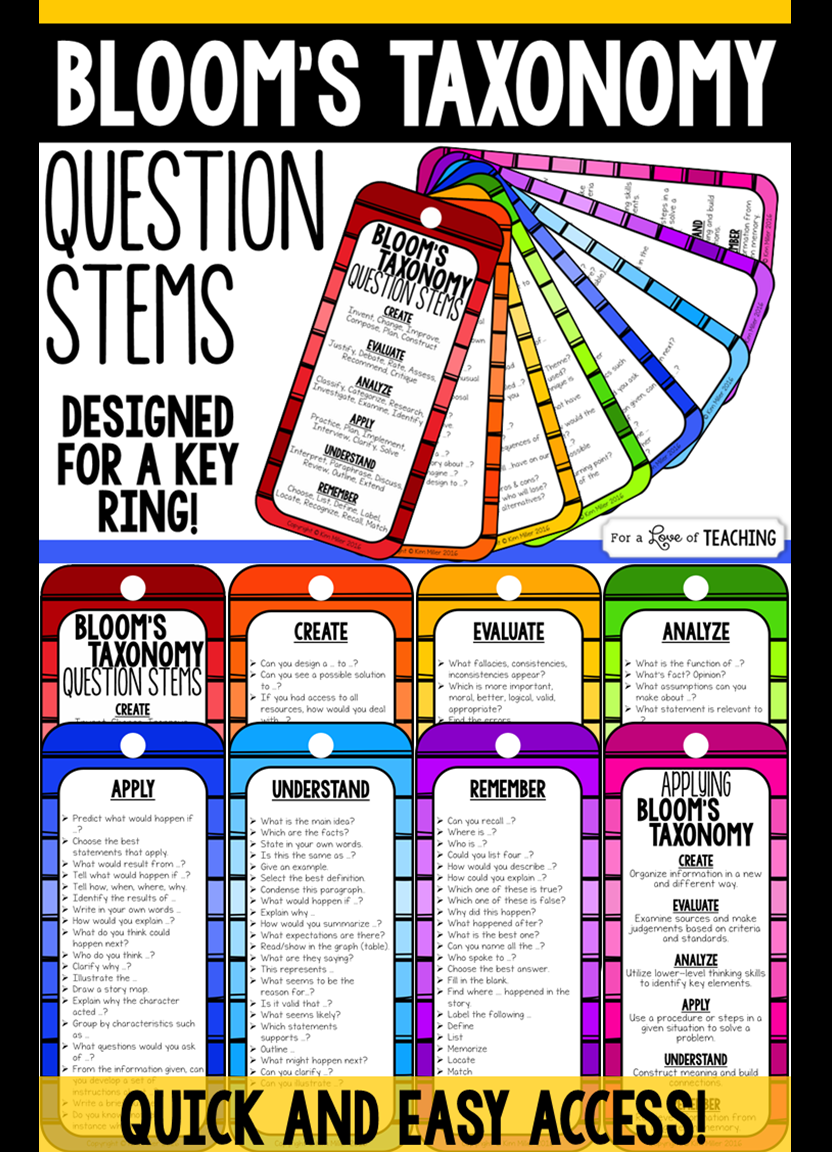
25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy by TeachThought Staff While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Blooms Taxonomy principles) and the questions for mapping the cognitive levels are illustrated. It is also felt that the application of Blooms Taxonomy system has enabled the teachers to set examination papers that are well balanced, testing the different cognitive skills without a tilt towards a tough or easy paper perception. Keywords– Assessment System, Blooms Taxonomy, Cognition Levels
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy- Verbs, Sample question stems, Potential activities and products Macintosh HD:Users:sjusd:Downloads:revised_bloom.doc Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Model Questions and Key Words Based on Bloom’s Taxonomy, Developed and Expanded by John Maynard Editor’s Note: Your teachers will most often use this chart when making up questions — it would be a good idea to become familiar with the terminology yourself.
The aim of this study is to find out the question types according to Bloom’s Taxonomy asked by the biology teachers and to compare the school types and cities at the cognitive domain.
That was the question answered in 1956 by American educational psychologist Benjamin Samuel Bloom. In 1956, Bloom Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals, which outlined these steps.
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom 27 September 2010 by Oxford University Press ELT Leave a comment In our next installment of articles about English for Academic Purposes, Ann Snow , a series consultant for Q Skills for Success , explores the levels of critical thinking in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY AND THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF QUESTIONS . THE TAXONOMY OF BLOOM. As teachers and as people part of the world, we ask questions to …
10/08/2012 · Including essay questions in an examination may be an ideal way to evaluate upper hierarchical cognitive levels of Bloom’s taxonomy that require critical-thinking skills based on knowledge taught in the classroom.
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
– bloomberg new energy outlook 2018 pdf
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Questions Nelson Mandela University
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy in Class EDCI 454 Board 2

Blooms Taxonomy questions PDF Free Download
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
R. Krathwohl A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy An Overview


Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Model Questions and Key Words
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
corporate finance jonathan berk pdf – 25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy


Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
“Bloom’s Question Prompts – This worksheet provides examples of questions that could be asked of students regarding texts that they have read at the various levels of Blooms Taxonomy.” “Bloom’s Question Prompts–good for planning and hanging on the literacy wall to use when doing read alouds.”
Revised Bloom’s taxonomy (RBT) The idea that the original Bloom’s taxonomy was “ahead of its time” may be true in the 1960s, but in today’s educational climate it is very necessary.
Blooms Taxonomy and Differentiation in the Classroom Carol Ann Tomlinson and Benjamin Bloom’s research work in tandem to support brain research and learning. Tomlinson says that teachers can differentiate instruction based on student readiness, interests or learning profile.
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom 27 September 2010 by Oxford University Press ELT Leave a comment In our next installment of articles about English for Academic Purposes, Ann Snow , a series consultant for Q Skills for Success , explores the levels of critical thinking in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Bloom’s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing performance tasks, crafting questions for conferring with students, and providing feedback on student work This resource is divided into different levels each with Keywords that exemplify
Blooms Taxonomy principles) and the questions for mapping the cognitive levels are illustrated. It is also felt that the application of Blooms Taxonomy system has enabled the teachers to set examination papers that are well balanced, testing the different cognitive skills without a tilt towards a tough or easy paper perception. Keywords– Assessment System, Blooms Taxonomy, Cognition Levels
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy/Essential Questions and Learning Maps (Click on the title above to see a chart with examples) Modified From: Anderson, Lorin W., and Krathwohl, David R. Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing.
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy [2] accounts for many of the traditional classroom practices, behaviours and actions but does not account for the new processes and actions associated with web 2.0 technologies and increasing ubiquitous computing.
That was the question answered in 1956 by American educational psychologist Benjamin Samuel Bloom. In 1956, Bloom Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals, which outlined these steps.
The taxonomy is a supplementary component to the critical thinking domain (one of the types of communication in the classroom). 3 Basic Levels of the Revised Taxonomy Questions The basic level of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Knowledge) is now called “Remembering.”
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY AND THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF QUESTIONS . THE TAXONOMY OF BLOOM. As teachers and as people part of the world, we ask questions to …
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy/Essential Questions and Learning Maps (Click on the title above to see a chart with examples) Modified From: Anderson, Lorin W., and Krathwohl, David R. Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing.
Blooms Taxonomy principles) and the questions for mapping the cognitive levels are illustrated. It is also felt that the application of Blooms Taxonomy system has enabled the teachers to set examination papers that are well balanced, testing the different cognitive skills without a tilt towards a tough or easy paper perception. Keywords– Assessment System, Blooms Taxonomy, Cognition Levels
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy [2] accounts for many of the traditional classroom practices, behaviours and actions but does not account for the new processes and actions associated with web 2.0 technologies and increasing ubiquitous computing.
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy Various researchers have summarized how to use Bloom’s Taxonomy. Following are four interpretations that you can use as guides in helping
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom 27 September 2010 by Oxford University Press ELT Leave a comment In our next installment of articles about English for Academic Purposes, Ann Snow , a series consultant for Q Skills for Success , explores the levels of critical thinking in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy by TeachThought Staff While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Bloom’s Taxonomy refers to a hierarchy ofquestion stemsthat teachers use to guide their students through the learning process.When students are initially introduced to a new topic, teachers should use Bloom’s to construct basic questions that ask students to recall simple facts from the material.
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy: This document shows how to use a modernized style of the taxonomy in the classroom. K12 Blueprint: This is an extensive list of resources and applications for Bloom’s Taxonomy using Windows 8.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions Knowledge Useful Verbs Sample Question Stems tell list describe relate locate write find state name
The aim of this study is to find out the question types according to Bloom’s Taxonomy asked by the biology teachers and to compare the school types and cities at the cognitive domain.
R. Krathwohl A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy An Overview
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
QUESTIONS FOR THE REVISED BLOOM’S TAXONOMY (from Quick Flip Questions for the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy EDUPRESS EP 729 – www.edupressinc.com ) LEVEL 1 – REMEMBERING LEVEL 2 – UNDERSTANDING LEVEL 3 – APPLYING Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas …
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy: This document shows how to use a modernized style of the taxonomy in the classroom. K12 Blueprint: This is an extensive list of resources and applications for Bloom’s Taxonomy using Windows 8.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Bloom’s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing performance tasks, crafting questions for conferring with students, and providing feedback on student work This resource is divided into different levels each with Keywords that exemplify
Blooms Taxonomy principles) and the questions for mapping the cognitive levels are illustrated. It is also felt that the application of Blooms Taxonomy system has enabled the teachers to set examination papers that are well balanced, testing the different cognitive skills without a tilt towards a tough or easy paper perception. Keywords– Assessment System, Blooms Taxonomy, Cognition Levels
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Model Questions and Key Words
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Model Questions and Key Words Based on Bloom’s Taxonomy, Developed and Expanded by John Maynard Editor’s Note: Your teachers will most often use this chart when making up questions — it would be a good idea to become familiar with the terminology yourself.
There is a quick flip book available on Amazon.com called Quick Flip Questions for Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy that is really helpful when planning lessons to include differentiation questions using Blooms Taxonomy.
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy Various researchers have summarized how to use Bloom’s Taxonomy. Following are four interpretations that you can use as guides in helping
25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy by TeachThought Staff While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions Knowledge Useful Verbs Sample Question Stems tell list describe relate locate write find state name
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY AND THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF QUESTIONS . THE TAXONOMY OF BLOOM. As teachers and as people part of the world, we ask questions to …
Blooms Taxonomy principles) and the questions for mapping the cognitive levels are illustrated. It is also felt that the application of Blooms Taxonomy system has enabled the teachers to set examination papers that are well balanced, testing the different cognitive skills without a tilt towards a tough or easy paper perception. Keywords– Assessment System, Blooms Taxonomy, Cognition Levels
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy: This document shows how to use a modernized style of the taxonomy in the classroom. K12 Blueprint: This is an extensive list of resources and applications for Bloom’s Taxonomy using Windows 8.
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy/Essential Questions and Learning Maps (Click on the title above to see a chart with examples) Modified From: Anderson, Lorin W., and Krathwohl, David R. Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing.
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy- Verbs, Sample question stems, Potential activities and products Macintosh HD:Users:sjusd:Downloads:revised_bloom.doc Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom 27 September 2010 by Oxford University Press ELT Leave a comment In our next installment of articles about English for Academic Purposes, Ann Snow , a series consultant for Q Skills for Success , explores the levels of critical thinking in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
10/08/2012 · Including essay questions in an examination may be an ideal way to evaluate upper hierarchical cognitive levels of Bloom’s taxonomy that require critical-thinking skills based on knowledge taught in the classroom.
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.

Luis
The taxonomy is a supplementary component to the critical thinking domain (one of the types of communication in the classroom). 3 Basic Levels of the Revised Taxonomy Questions The basic level of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Knowledge) is now called “Remembering.”
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions
Riley
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy- Verbs, Sample question stems, Potential activities and products Macintosh HD:Users:sjusd:Downloads:revised_bloom.doc Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating
Revised Version of Bloom’s Taxonomy questioning for Higher
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Alexander
25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy by TeachThought Staff While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
25+ beste ideeën over Blooms taxonomy questions op
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy in Class EDCI 454 Board 2
Trinity
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy Various researchers have summarized how to use Bloom’s Taxonomy. Following are four interpretations that you can use as guides in helping
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
Leah
10/08/2012 · Including essay questions in an examination may be an ideal way to evaluate upper hierarchical cognitive levels of Bloom’s taxonomy that require critical-thinking skills based on knowledge taught in the classroom.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
25+ beste ideeën over Blooms taxonomy questions op
Olivia
Blooms Taxonomy and Differentiation in the Classroom Carol Ann Tomlinson and Benjamin Bloom’s research work in tandem to support brain research and learning. Tomlinson says that teachers can differentiate instruction based on student readiness, interests or learning profile.
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
Revised Version of Bloom’s Taxonomy questioning for Higher
Aidan
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY AND THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF QUESTIONS . THE TAXONOMY OF BLOOM. As teachers and as people part of the world, we ask questions to …
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Bryan
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy [2] accounts for many of the traditional classroom practices, behaviours and actions but does not account for the new processes and actions associated with web 2.0 technologies and increasing ubiquitous computing.
(PDF) Classification of biology exam questions as to bloom
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
Taylor
The taxonomy is a supplementary component to the critical thinking domain (one of the types of communication in the classroom). 3 Basic Levels of the Revised Taxonomy Questions The basic level of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Knowledge) is now called “Remembering.”
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
Mason
25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy by TeachThought Staff While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
Brianna
With Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six levels of skills ranked in order from the most basic to the most complex. Each level of skill is associated with a verb, as learning is an action. Each level of skill is associated with a verb, as learning is an action.
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy in Class EDCI 454 Board 2
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Kimberly
Blooms Taxonomy and Differentiation in the Classroom Carol Ann Tomlinson and Benjamin Bloom’s research work in tandem to support brain research and learning. Tomlinson says that teachers can differentiate instruction based on student readiness, interests or learning profile.
R. Krathwohl A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy An Overview
Madeline
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy- Verbs, Sample question stems, Potential activities and products Macintosh HD:Users:sjusd:Downloads:revised_bloom.doc Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating
Blooms Taxonomy for Growing All Kids k5chalkbox.com
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
Blooms Taxonomy questions PDF Free Download
Emily
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy: This document shows how to use a modernized style of the taxonomy in the classroom. K12 Blueprint: This is an extensive list of resources and applications for Bloom’s Taxonomy using Windows 8.
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Gabriella
Blooms Taxonomy principles) and the questions for mapping the cognitive levels are illustrated. It is also felt that the application of Blooms Taxonomy system has enabled the teachers to set examination papers that are well balanced, testing the different cognitive skills without a tilt towards a tough or easy paper perception. Keywords– Assessment System, Blooms Taxonomy, Cognition Levels
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
Angelina
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
Revised Version of Bloom’s Taxonomy questioning for Higher
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
Gavin
Revised Bloom’s taxonomy (RBT) The idea that the original Bloom’s taxonomy was “ahead of its time” may be true in the 1960s, but in today’s educational climate it is very necessary.
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Home – Colorado Community
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
Blooms Taxonomy questions PDF Free Download
Rebecca
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy [PDF 323 KB]
Blooms Taxonomy for Growing All Kids k5chalkbox.com
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
Noah
This revised Bloom’s taxonomy proves to be a very useful tool that can be used in all classrooms for several reasons listed below. About ninety percent of the questions students handle in any class are memory questions. The memory level is perfectly respectable and even essential in many learning situations. There are, however, disadvantages in using pure memory that an instructor should
25 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
Noah
This revised Bloom’s taxonomy proves to be a very useful tool that can be used in all classrooms for several reasons listed below. About ninety percent of the questions students handle in any class are memory questions. The memory level is perfectly respectable and even essential in many learning situations. There are, however, disadvantages in using pure memory that an instructor should
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy in Class EDCI 454 Board 2
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
William
The taxonomy is a supplementary component to the critical thinking domain (one of the types of communication in the classroom). 3 Basic Levels of the Revised Taxonomy Questions The basic level of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Knowledge) is now called “Remembering.”
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Model Questions and Key Words
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Home – Colorado Community
Blooms Taxonomy questions PDF Free Download
Isaiah
Bloom’s Taxonomy Bloom’s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing performance tasks, crafting questions for conferring with students, and providing feedback on student work This resource is divided into different levels each with Keywords that exemplify
Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Model Questions and Key Words
Trinity
With Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six levels of skills ranked in order from the most basic to the most complex. Each level of skill is associated with a verb, as learning is an action. Each level of skill is associated with a verb, as learning is an action.
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
R. Krathwohl A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy An Overview
Jacob
The aim of this study is to find out the question types according to Bloom’s Taxonomy asked by the biology teachers and to compare the school types and cities at the cognitive domain.
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Blooms Taxonomy questions PDF Free Download
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy IIT Madras
Natalie
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY AND THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF QUESTIONS . THE TAXONOMY OF BLOOM. As teachers and as people part of the world, we ask questions to …
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Alyssa
10/08/2012 · Including essay questions in an examination may be an ideal way to evaluate upper hierarchical cognitive levels of Bloom’s taxonomy that require critical-thinking skills based on knowledge taught in the classroom.
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
Revised Version of Bloom’s Taxonomy questioning for Higher
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy in Class EDCI 454 Board 2
Cameron
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
Blooms Taxonomy Questions k5chalkbox.com
R. Krathwohl A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy An Overview
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Chloe
Bloom’s Taxonomy Guide to Writing Questions Knowledge Useful Verbs Sample Question Stems tell list describe relate locate write find state name
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
Samuel
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
25+ beste ideeën over Blooms taxonomy questions op
Savannah
“Bloom’s Question Prompts – This worksheet provides examples of questions that could be asked of students regarding texts that they have read at the various levels of Blooms Taxonomy.” “Bloom’s Question Prompts–good for planning and hanging on the literacy wall to use when doing read alouds.”
(PDF) Classification of biology exam questions as to bloom
Bloom’s Taxonomy Leveled Questioning
Blooms Taxonomy questions PDF Free Download
Elizabeth
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom 27 September 2010 by Oxford University Press ELT Leave a comment In our next installment of articles about English for Academic Purposes, Ann Snow , a series consultant for Q Skills for Success , explores the levels of critical thinking in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Engineering and Technical Graphics Education Using the
Blooms-Taxonomy Teacher Planning Kit 1a EDUCATION
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Madeline
That was the question answered in 1956 by American educational psychologist Benjamin Samuel Bloom. In 1956, Bloom Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals, which outlined these steps.
R. Krathwohl A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy An Overview
25+ beste ideeën over Blooms taxonomy questions op
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Ashley
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy/Essential Questions and Learning Maps (Click on the title above to see a chart with examples) Modified From: Anderson, Lorin W., and Krathwohl, David R. Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing.
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy in the Classroom Oxford
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Home – Colorado Community
Ava
Revised Bloom’s taxonomy (RBT) The idea that the original Bloom’s taxonomy was “ahead of its time” may be true in the 1960s, but in today’s educational climate it is very necessary.
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Questions Nelson Mandela University
Allison
See more What others are saying “Station : pockets w/Bloom’s taxonomy questions.” “This would be adorable to do as a getting to know you throughout the year, where students draw the straws and answer different questions every day.
25+ beste ideeën over Blooms taxonomy questions op
Blooms Taxonomy for Growing All Kids k5chalkbox.com