Benjamin bloom taxonomy of educational objectives pdf
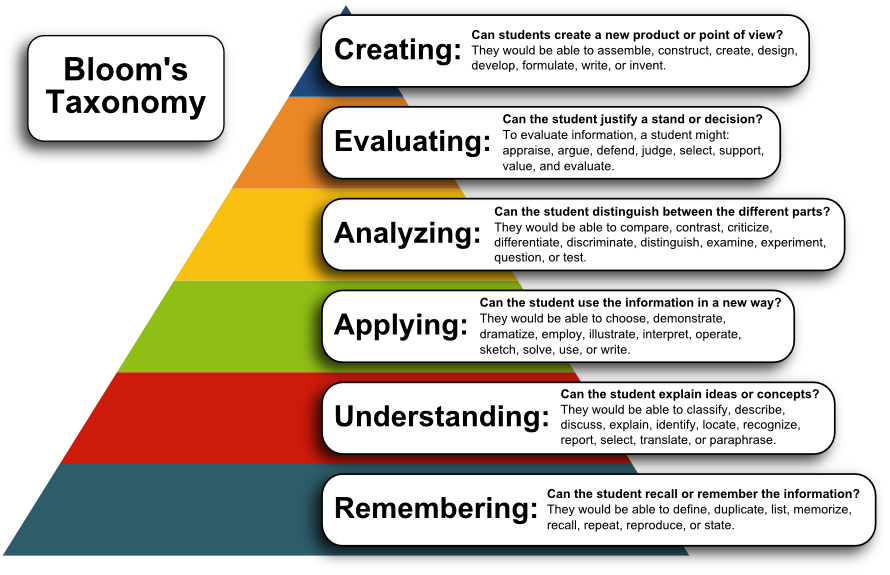
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework for organizing evidence of learning into levels of complexity and maturity. Published in 1956, the tool was named for professor Benjamin Bloom, who was the first author of the taxonomy developed by 34 scholars at a series of APA conferences between 1949 and 1953. Revised in 2002, it is one of the most widely utilized tools in K-12 and higher education
Benjamin Bloom classified educational objectives and their evaluation process into three domains for effective learning outcomes. Cognitive domain involves intellectual skills whereas
Benjamin Bloom. 240 likes. Benjamin Samuel Bloom was an American educational psychologist who made contributions to the classification of educational…
These various levels are defined in Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomies or classification systems of educational objectives: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Cognitive objectives emphasize memory and reasoning, affective objectives emphasize emotional, and
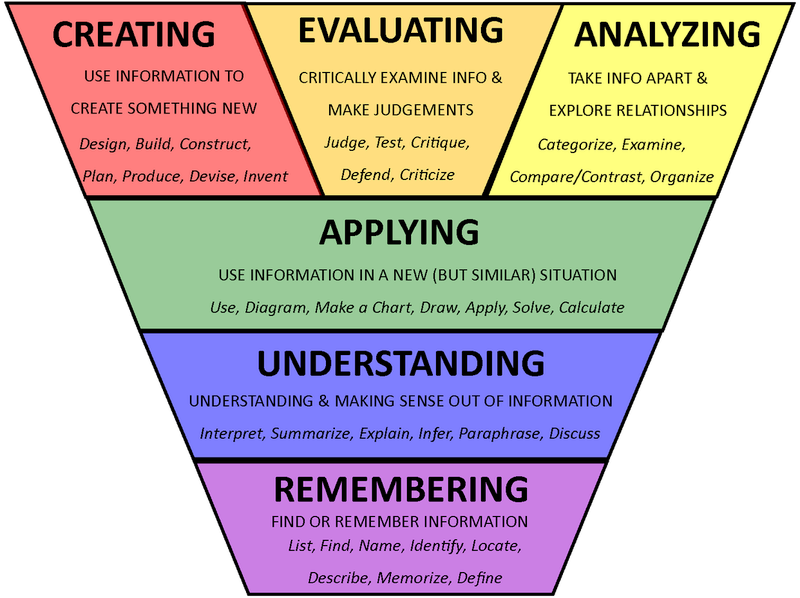
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Critical Thinking and Writing Effective Learning Objectives/Outcomes In 1956 Benjamin S. Bloom and his colleagues outlined six levels of critical thinking into which any cognitive learning experience may be categorized. Beginning with
of the famed Benjamin Bloom, and David Krathwohl was one of Bloom’s partners as he devised his classic cognitive taxonomy. Here in the United States, from the late 1950s into the early 1970s, there were attempts to dissect and classify the varied domains of human learning – cognitive (knowing, or head), affective (emotions, feelings, or heart) and psychomotor (doing, or kinesthetic
Benjamin Bloom’s eponymous taxonomy emerged from a series of informal discussions with colleagues that began at the American Psychological Association in 1948. He actually intended his work for a narrow audience: assessment experts who were developing new ways to measure what college students learned. But Bloom’s Taxonomy became the most widely used method of creating learning objectives
Bloom’s Taxonomy has thus been specialized and expanded to include the kinds of verbs used to describe learning objectives typically encountered in an engineering education…
Benjamin Bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior important in learning.uct.htm] MCQs and Bloom’s Taxonomy [Cape Town. Bloom took a lead in formulating a classification of “the goals of the educational process”. B..wested. www.wwu. and affective. SA: UCT’s page on Designing and Managing Multiple Choice Questions.” Bloom
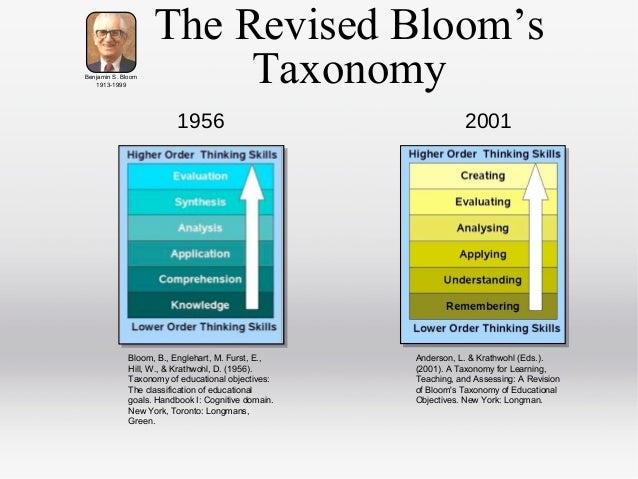
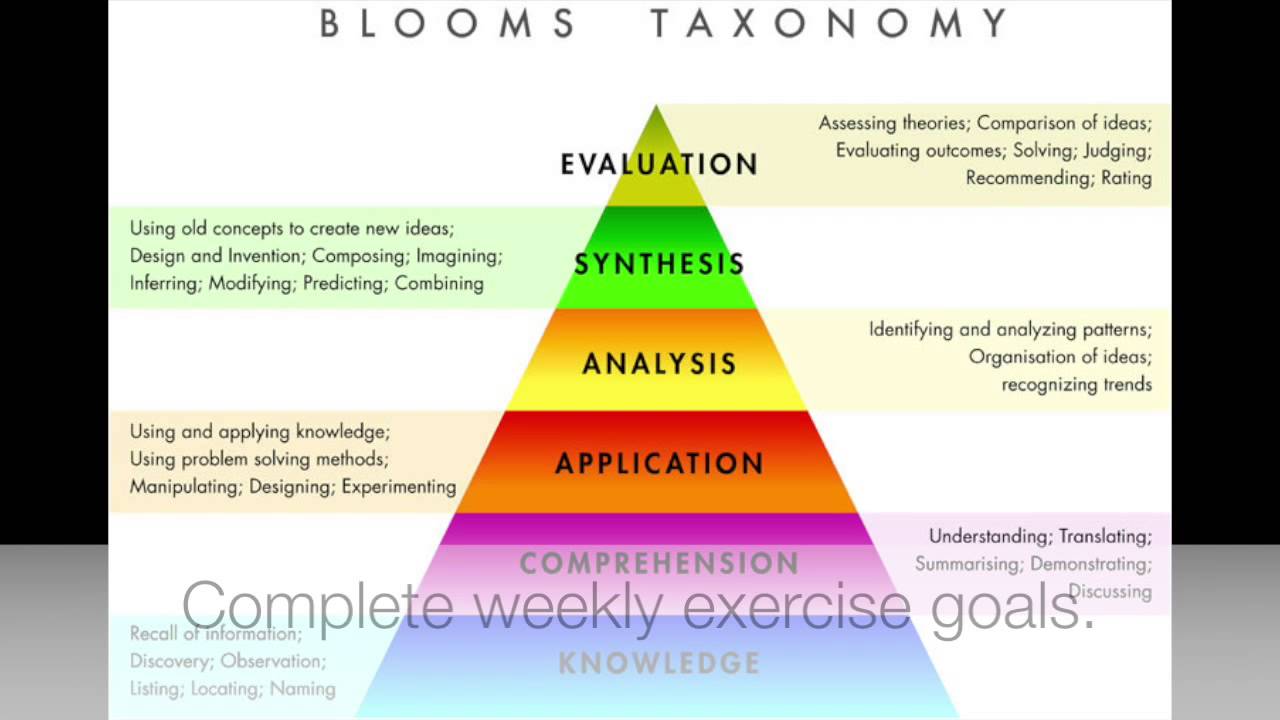
The Need for a Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy I n 1956, a small, somewhat technical volume was published under the title,Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, The Classification of Educational Goals, Handbook I : Cognitive Domain (Bloom et al., 1956). In the 50-plus years since its publication, “Bloom’s Taxonomy,” as it is frequently referred to in deference to Benjamin Bloom, the work’s
Taxonomies of Educational Objective Domain Eman Ghanem Nayef 1, Bloom’s taxonomy Benjamin Bloom developed the Taxonomy of Cognitive Objectives in the 1950s by qualitatively expressing different types of thinking. Benjamin Samuel Bloom was born on February 21, 1913 in Lansford, Pennsylvania, USA. He earned his bachelors and masters degrees from the Pennsylvania …
While Bloom pushed for the use of the term “taxonomy,” others in the group resisted because of the unfamiliarity of the term within educational circles. Eventually Bloom prevailed, forever linking hi s name and the term.
Educational Objectives Bloom Educational Psychology
Benjamin Bloom Local Business Facebook
how Benjamin Bloom’s personal life directly influenced his development of the taxonomy, but, more importantly, this will examine how his taxonomy research led him to more influential and meaningful theories about education and the roles of the student
Benjamin Bloom was an American educational psychologist whose life’s work centered on the theory of mastery learning, the classification of educational objectives, and early childhood education.
Bloom’s Taxonomy was originally created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956. This is an invaluable tool that will help you write This is an invaluable tool that will help you write learning outcomes, develop assignments, create a training module, ask effective questions, and design activities.
Taxonomy • Taxonomy of Cognitive Objectives • 1950s- developed by Benjamin Bloom • Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking • Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool • Continues to be one of the most universally applied models • Provides a way to organise thinking skills into six levels, from the most basic to the more complex levels of thinking
2 Original Bloom’s Taxonomy In 1956, Benjamin Bloom with other collaborators published a framework for categorizing educational goals called, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
Benjamin Samuel Bloom (February 21, 1913 – September 13, 1999) was an American educational psychologist who made contributions to the classification of educational objectives and to the theory of mastery learning.
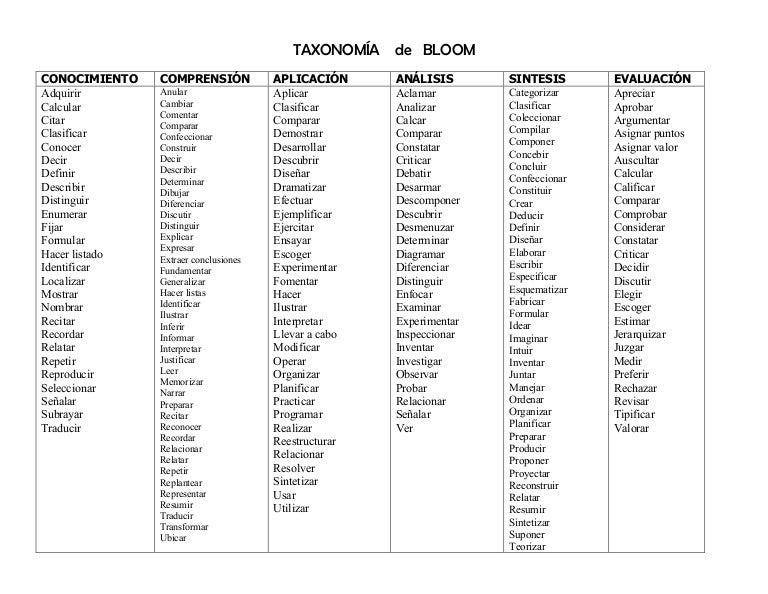
educational objectives pdf – Bloom’s taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive, affective and sensory domains. The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum
Benjamin S. Bloom was an American educational psychologist who has made contributions to the classification of educational objectives and to the theory of mastery-learning. Books by Benjamin S. Bloom …
educational objectives: Handbook 1, the cognitive domain (Bloom et al., 1956), a publication that has been used throughout the world to assist in the preparation of evaluation materials. The cognitive taxonomy is predicated on the idea that cognitive operations can be
Benjamin Bloom (1948) developed classifications of intellectual behavior and learning in order to identify and measure progressively sophisticated learning. College faculty are hired because of their discipline expertise and are sometimes unfamiliar with important pedagogical theories that contribute to effective learning. Bloom’s taxonomy is especially important in higher education where

committee of educators chaired by Benjamin Bloom who also edited the first volume of the standard text, Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals[1] (1956).[2
The taxonomy was first presented in 1956 through the publication The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, The Classification of Educational Goals, Handbook I: Cognitive Domain, by Benjamin Bloom (editor), M. D. Englehart, E. J. Furst, W. H. Hill, and David Krathwohl. It is considered to be a foundational and essential element within the education community as evidenced in the 1981 survey
Benjamin S. Bloom was an American educational psychologist who has made contributions to the classification of educational objectives and to the theory of mastery-learning.
In the 1950’s, Dr. Benjamin Bloom categorized a list of educational objectives that is now known as “Bloom’s Taxonomy.” Bloom’s Taxonomy can help
CONSTRUCTIVISM & STUDENT CENTERED LEARNING 9. BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
– instructions for making doll bloomers
WikiZero Benjamin Bloom
Higher-Order Thinking Skills

Bloom’s Taxonomy oregon.gov
Running head INFLUENCES ON BLOOM’S TAXONOMY 1 Influences
Benjamin Bloom International Centre for Educators’ Styles
secrets of professional tournament poker volume 2 jonathan little pdf –

Trinity
In the 1950’s, Dr. Benjamin Bloom categorized a list of educational objectives that is now known as “Bloom’s Taxonomy.” Bloom’s Taxonomy can help
Educational Objectives Bloom Educational Psychology
Bloom’s Taxonomy csus.edu
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
David
2 Original Bloom’s Taxonomy In 1956, Benjamin Bloom with other collaborators published a framework for categorizing educational goals called, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
Bloom and Learning Objectives Handout ctl.yale.edu
Isaiah
Benjamin Bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior important in learning.uct.htm] MCQs and Bloom’s Taxonomy [Cape Town. Bloom took a lead in formulating a classification of “the goals of the educational process”. B..wested. http://www.wwu. and affective. SA: UCT’s page on Designing and Managing Multiple Choice Questions.” Bloom
Bloom’s Taxonomy oregon.gov
Stephanie
Taxonomy • Taxonomy of Cognitive Objectives • 1950s- developed by Benjamin Bloom • Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking • Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool • Continues to be one of the most universally applied models • Provides a way to organise thinking skills into six levels, from the most basic to the more complex levels of thinking
CONSTRUCTIVISM & STUDENT CENTERED LEARNING 9. BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
Benjamin Bloom Local Business Facebook
Juan
These various levels are defined in Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomies or classification systems of educational objectives: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Cognitive objectives emphasize memory and reasoning, affective objectives emphasize emotional, and
Running head INFLUENCES ON BLOOM’S TAXONOMY 1 Influences
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
WikiZero Benjamin Bloom
Jessica
These various levels are defined in Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomies or classification systems of educational objectives: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Cognitive objectives emphasize memory and reasoning, affective objectives emphasize emotional, and
WikiZero Benjamin Bloom
Faith
Benjamin S. Bloom was an American educational psychologist who has made contributions to the classification of educational objectives and to the theory of mastery-learning.
Appendix Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
Bloom and Learning Objectives Handout ctl.yale.edu
Bloom’s Taxonomy csus.edu
Bryan
Benjamin Bloom was an American educational psychologist whose life’s work centered on the theory of mastery learning, the classification of educational objectives, and early childhood education.
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
Jasmine
While Bloom pushed for the use of the term “taxonomy,” others in the group resisted because of the unfamiliarity of the term within educational circles. Eventually Bloom prevailed, forever linking hi s name and the term.
Benjamin S. Bloom (Author of Taxonomy of Educational
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
Kyle
educational objectives: Handbook 1, the cognitive domain (Bloom et al., 1956), a publication that has been used throughout the world to assist in the preparation of evaluation materials. The cognitive taxonomy is predicated on the idea that cognitive operations can be
Running head INFLUENCES ON BLOOM’S TAXONOMY 1 Influences
Benjamin Bloom International Centre for Educators’ Styles
CONSTRUCTIVISM & STUDENT CENTERED LEARNING 9. BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
Abigail
2 Original Bloom’s Taxonomy In 1956, Benjamin Bloom with other collaborators published a framework for categorizing educational goals called, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
CONSTRUCTIVISM & STUDENT CENTERED LEARNING 9. BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
Benjamin Bloom International Centre for Educators’ Styles
Lucas
In the 1950’s, Dr. Benjamin Bloom categorized a list of educational objectives that is now known as “Bloom’s Taxonomy.” Bloom’s Taxonomy can help
WikiZero Benjamin Bloom
Benjamin Bloom Local Business Facebook
Bloom’s Taxonomy oregon.gov
Joseph
The taxonomy was first presented in 1956 through the publication The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, The Classification of Educational Goals, Handbook I: Cognitive Domain, by Benjamin Bloom (editor), M. D. Englehart, E. J. Furst, W. H. Hill, and David Krathwohl. It is considered to be a foundational and essential element within the education community as evidenced in the 1981 survey
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
Mason
These various levels are defined in Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomies or classification systems of educational objectives: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Cognitive objectives emphasize memory and reasoning, affective objectives emphasize emotional, and
Running head INFLUENCES ON BLOOM’S TAXONOMY 1 Influences
Bloom’s Taxonomy csus.edu
Trinity
Benjamin Bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior important in learning.uct.htm] MCQs and Bloom’s Taxonomy [Cape Town. Bloom took a lead in formulating a classification of “the goals of the educational process”. B..wested. http://www.wwu. and affective. SA: UCT’s page on Designing and Managing Multiple Choice Questions.” Bloom
Appendix Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
Samuel
The Need for a Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy I n 1956, a small, somewhat technical volume was published under the title,Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, The Classification of Educational Goals, Handbook I : Cognitive Domain (Bloom et al., 1956). In the 50-plus years since its publication, “Bloom’s Taxonomy,” as it is frequently referred to in deference to Benjamin Bloom, the work’s
Benjamin Bloom Local Business Facebook
Appendix Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
Applying Bloom’s Taxonomy to Game Design
Isabella
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework for organizing evidence of learning into levels of complexity and maturity. Published in 1956, the tool was named for professor Benjamin Bloom, who was the first author of the taxonomy developed by 34 scholars at a series of APA conferences between 1949 and 1953. Revised in 2002, it is one of the most widely utilized tools in K-12 and higher education
Appendix Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
Isaac
Benjamin Bloom was an American educational psychologist whose life’s work centered on the theory of mastery learning, the classification of educational objectives, and early childhood education.
Benjamin S. Bloom (Author of Taxonomy of Educational
Diego
Taxonomy • Taxonomy of Cognitive Objectives • 1950s- developed by Benjamin Bloom • Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking • Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool • Continues to be one of the most universally applied models • Provides a way to organise thinking skills into six levels, from the most basic to the more complex levels of thinking
WikiZero Benjamin Bloom
Benjamin Bloom Local Business Facebook
Cole
Bloom’s Taxonomy was originally created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956. This is an invaluable tool that will help you write This is an invaluable tool that will help you write learning outcomes, develop assignments, create a training module, ask effective questions, and design activities.
Bloom and Learning Objectives Handout ctl.yale.edu
Educational Objectives Bloom Educational Psychology
Running head INFLUENCES ON BLOOM’S TAXONOMY 1 Influences
Sara
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Critical Thinking and Writing Effective Learning Objectives/Outcomes In 1956 Benjamin S. Bloom and his colleagues outlined six levels of critical thinking into which any cognitive learning experience may be categorized. Beginning with
Benjamin Bloom International Centre for Educators’ Styles
WikiZero Benjamin Bloom
Appendix Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
Sarah
Benjamin Bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior important in learning.uct.htm] MCQs and Bloom’s Taxonomy [Cape Town. Bloom took a lead in formulating a classification of “the goals of the educational process”. B..wested. http://www.wwu. and affective. SA: UCT’s page on Designing and Managing Multiple Choice Questions.” Bloom
Benjamin Bloom International Centre for Educators’ Styles