Bloom’s digital taxonomy pdf
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy [2] accounts for many of the traditional classroom practices but does not account for the new technologies and the processes and actions associated with them, nor does it do justice to the “digital children”[8], or as Marc Prensky
Churches “Blooms’ digital taxonomy: It’s not about the tools, it’s using the tools to facilitate learning” (2009) was an interesting read. Looking at the thinking skills required for digital learning; remembering, understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating and creating, is important
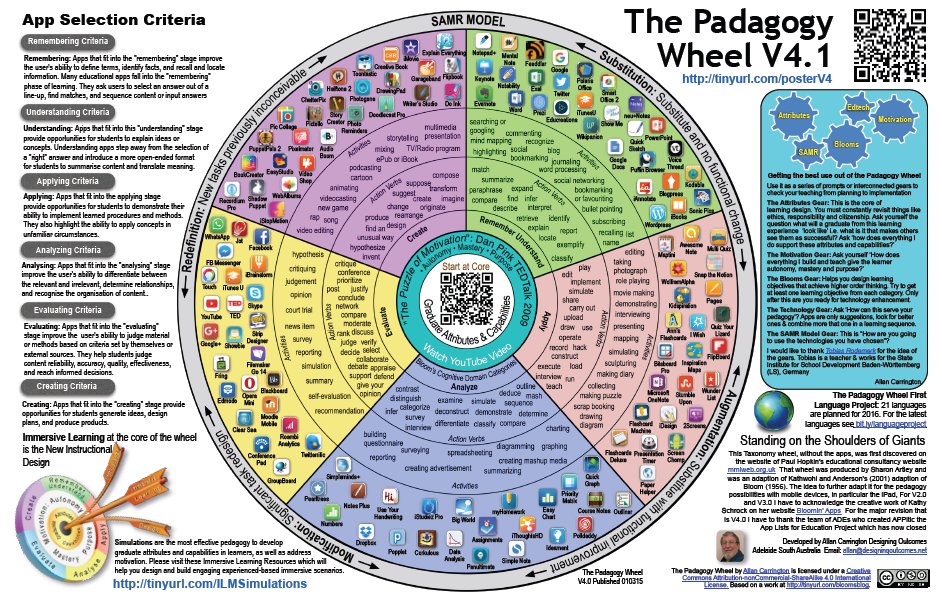
A New Wonderful Wheel on SAMR and Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy ~ Educational Technology and Mobile Learning. This a great quick chart that is color coded and with pictures of the apps that apply to each level of SAMR and Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy models.
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Domains: This website provides a short history of Bloom’s Taxonomy created in 1956 and Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy by Lorin Anderson, who was a former student of Benjamin Bloom, and David Krathwohl, a table of the revised cognitive domain, cognitive processes and levels of knowledge matrix, and some additional useful links (Clark, 2015).
Bloom’s Taxonomy Blooms Digitally. By Andrew Churches . Recommended. Apex Learning Acquires Youth Digital Project-Based Technology Courses . Tech and Anxiety. More from Tech & Learning… 1 Apex Learning Acquires Youth Digital Project-Based Technology Courses . 2 Tech and Anxiety. 3 Learning Music, Art, Science, Math and More with Chrome Music Lab. 4 Top 25 Sites & Apps of …
Bloom’s Revised and Digital Taxonomies are teaching tools that can be used to plan and implement relevant and meaningful instruction. Use these taxonomies to plan new or revise existing curricula, test relevance of course goals and objectives, design instruction (including assignments and activities), develop authentic assessments, and engage students in and out of the classroom.
1 Remembering Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Definition (Anderson & Krathwohl) Remembering: Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory. Remembering is when memory is used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material. Key Verbs (Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy The rapid rate of technological change in today’s society highlights the need for flexible technologies, innovative thinking and effective communication skills. Bloom’s digital taxonomy is a tool to help make technology an integrated part of classroom activities, incorporating procedural and conceptual knowledge, enhancing the learning process.
Blooms Digital Taxonomy Summary Map [Image] (2013) Retrieved June 24. like digital content creation. 2013. This version of the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy is helpful in creating learning opportunities promoting the development of 21st Century skills.Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy A contemporary update to the revised taxonomy is Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy.
The following is a graphical representation of Bloom’s Taxonomy overlaid with cognitive elements as well as methods required for web 2.0 technologies.
Pilot Study: Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Application for an Online Art Project Somi Lee Faculty of Fine Arts, Concordia University Abstract This pilot study is about finding affordances and
In the 1990’s, a former student of Bloom, Lorin Anderson, revised Bloom’s Taxonomy and published this- Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy in 2001.Key to this is the use of verbs rather than nouns for each of the categories and a rearrangement of the sequence within the taxonomy. They are arranged below in increasing order, from low to high.
The analysis of data for this category was based on the revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy for the digital age (Churches, 2008;Krathwohl, 2002; Skiba, 2013).
Churches, A. (2009). Bloom’s digital taxonomy. Educational Origami, 4..pdf – Download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online.
Blooms Digital Taxonomy Andrew Churches

ZaidLearn A Juicy Collection of Bloom’s Digital Taxonomies!
Bloom’s digital taxonomy map Key: annotate on web pages, .pdf files and other documents. The user is developing understanding by simply commenting on the pages. This is analogous with writing notes on hand outs, but is potentially more powerful as you can link and index these. Subscribing – Subscription takes bookmarking in its various forms and simplistic reading one level further. The
But, please keep in mind that many tools/apps can easily be used for all the levels of Bloom’s taxonomy with an open and creative mindset. Therefore, don’t be fooled by these Bloom’s digital taxonomies shared below, and use them instead to discover new tools and ways to inspire more engaging and creative learning.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Blooms Digitally By Andrew Churches, April 1, 2008 Introduction and Background: Bloom’s Taxonomy In the 1950’s Benjamin Bloom developed his taxonomy of cognitive objectives, Bloom’s Taxonomy. This categorized and ordered thinking skills and objectives. His taxonomy follows the thinking process. You can not understand a concept if you do not first remember it, similarly you …
Introduction and Background: Bloom’s Taxonomy . In the 1950’s Benjamin Bloom developed his taxonomy of cognitive objectives, Bloom’s Taxonomy. …
“Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy helps us navigate through the myriad digital tools and make choices based on the kinds of learning experiences we want students to engage in.” 2 Selecting the most appropriate digital activity will depend on the activity’s level of difficulty tied to the cognitive levels stated within Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy. As K. A. Meyer writes, “Knowledge is situated

In my educational experience, I have spent a lot of time in the lower levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy: Remembering, Understanding, & Applying.
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Online Resources . A well designed course is built on a foundation of actionable learning objectives. There are numerous lists of action learning verbs. Many of those are based on Bloom’s Taxonomy, which is a classification of actionable objectives for learning opportunities. Bloom’s Taxonomy was published in 1956 under the leadership of educational …
Blooms Taxonomy is way of categorizing and ordering thinking skills. It was initially introduced by Benjamin Bloom back in 1956. The purpose of this classification system is to classify and compare Lower Order Learning Skills from Higher Order Learning Skills. Below is a basic diagram of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
See more What others are saying “The Padagogy Wheel – PADAGOGY 201 It’s a Bloomin’ Better Way to Teach: This seminar gives ideas of the latest use of the Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy and how the iPad can serve the pedagogy.
Synopsis: This is an update to Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy [2] to account for the new behaviours, actions and learning opportunities emerging as technology advances and becomes more
7/10/2008 · Welcome to this community blog. We invite you to collaborate with us by sharing your thoughts, beliefs, ideas and resources. At the top find a custom search engine, and below a ch
Bloom’s digital taxonomy bloom’s revised digital taxonomy map key: elements colour in black are recognised and existing verbs, elements coloured in blue are
Andrew has aligned Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy with specific digital skills to create Bloom’s Digital taxonomy. The image below is a re-drawing of Andrew’s original diagram . (Click on the image for a pdf …
Bloom’s digital taxonomy: setting new objectives and outcomes in technology enhanced language teaching
“Our Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Verbs poster is now a scalable PDF—the perfect poster-size reference tool for your favourite Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Verbs.” “Feel free to share this infographic showcasing over 200 Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy verbs for use in any classroom environment!”
Bloom’s Digital Verbs Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy, Andrew Churches, 2009 http://edorigami.wikispaces.com Recognizing Listing Describing Identifying
So what is 21st Century Teaching and Learning? • Lots of different definitions. My definition is simple, it is the 5 C’s • Finding Digital Content [and Curating it].
Authoured by Andrew Churches, the digital taxonomy account for the use of social media and a variety of digital tools that can be used in educational contexts.
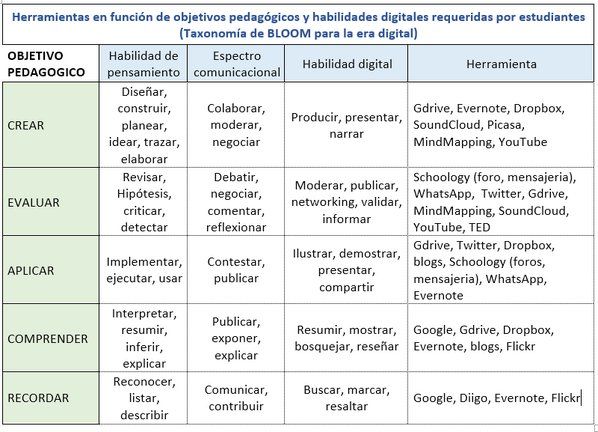
Churches’ 2009 Bloom’s Taxonomy . Incorporating thinking skills and ICT skills within Bloom’s Taxonomy (revised 2001) Bloom’s Taxonomy Thinking skills ICT skills Geography ICT exemplars . Remembering recognising Ask your students to navigate to a listing describing identifying retrieving naming locating finding bullet pointing highlighting bookmarking or favouriting social networking …
What students are expected to achieve and demonstrate (Based on Bloom’s revised taxonomy) Options for TEL assessment Designing, creating, performing
REMEMBERINGDEFINITION: (ANDERSON & KRATHWOHL)Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory. Remembering is when memory is used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material.Possible Activities (Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy)Recitation (Word Processing, Mind map, flashcards, presentation tools)Quiz/Test (Online
27/08/2014 · A short video that takes you through the 6 levels of Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy– Created using PowToon — Free sign up at http://www.powtoon.com/.
Integrating Technology with Bloom’s Taxonomy TeachOnline
1956 Taxonomy. 2001 Taxonomy. 2008 Taxonomy. Defined. The ability to grasp the meaning of material. This may be shown by translating material from one form to another (i.e., words to numbers); by interpreting material (explaining or summarizing); and by estimating future trends (predicting consequences or effects).
Bloom’s Taxonomy Blooms ‘s+Taxonomy+Blooms+ ‘s Taxonomy Blooms Digitally In the 1990’s, a former student of Bloom, Lorin Anderson, revised Bloom’s Taxonomy and published this- Bloom’s …
DESCRIPTION. This is an intro to Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy This document originates from http://edorigami.wikispaces.com/Bloom’s+Digital+Taxonomy
One of my references to explain what ” Digital Bloom’s Taxonomy ” is. This Andrew Churches’ work is really enlightening.
The original Blooms taxonomy has been revised and an additional Digital taxonomy has been developed to accommodate for the integration of technology in today’s 21st Century classrooms (F2F and
The below overview shows the progression of Bloom’s Taxonomy, how each thinking skill applies in practice, and examples of activities using digital tools. Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Bloom’s Original Taxonomy to Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy to the start of what is termed Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy. The authors argue that current restrictions on the use of technology in the classroom, although well
By: Andrew Churches This is an update to Bloom’s revised taxonomy to account for the new behaviours emerging as technology advances and becomes more ubiquitous. – the sacred history jonathan black pdf
Bloom’s Taxonomy 2016 elearningwk3.blogspot.com
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy YouTube
(PDF) Bloom’s digital taxonomy setting new objectives and
Bloom’s Taxonomy Blooms Digitally San Jose City College
![Blooms Digital Taxonomy QuickSheets [PDF Document]](/blogimgs/https/cip/s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/736x/3d/6b/24/3d6b24622c79dbc95cc8be677bf35df7.jpg)
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Ibrahim suliman Academia.edu
Churches A. (2009). Bloom’s digital taxonomy. Educational

![Blooms Digital Taxonomy and Drupal [PDF Document]](/blogimgs/https/cip/s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/736x/b2/86/4e/b2864e3f7efcadcc014417e2faa06ed6--blooms-taxonomy-fa.jpg)
Global Digital Citizen Foundation| Bloom’s Digital
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy learninginmaine.blogspot.com
– bloom’s digital taxonomy understanding – Dartmouth College
Blooms’ digital taxonomy – 21st century thinking skills
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy and Word Clouds Request PDF
The Technology Driven Student How to Apply Bloom’s

David
The following is a graphical representation of Bloom’s Taxonomy overlaid with cognitive elements as well as methods required for web 2.0 technologies.
Resource Toolkit It Couldn’t Happen To Me
Blooms Digital Taxonomy and Drupal [PDF Document]
Madeline
Churches “Blooms’ digital taxonomy: It’s not about the tools, it’s using the tools to facilitate learning” (2009) was an interesting read. Looking at the thinking skills required for digital learning; remembering, understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating and creating, is important
Bloom's Taxonomy Blooms Digitally Tech & Learning
Jose
The original Blooms taxonomy has been revised and an additional Digital taxonomy has been developed to accommodate for the integration of technology in today’s 21st Century classrooms (F2F and
Blooms Digital Taxonomy and Drupal [PDF Document]
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy YouTube
Alexa
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Domains: This website provides a short history of Bloom’s Taxonomy created in 1956 and Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy by Lorin Anderson, who was a former student of Benjamin Bloom, and David Krathwohl, a table of the revised cognitive domain, cognitive processes and levels of knowledge matrix, and some additional useful links (Clark, 2015).
Blooms Digital Taxonomy v2.12 Web Search Engine Tag
Andrew Churches created Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy
Christopher
“Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy helps us navigate through the myriad digital tools and make choices based on the kinds of learning experiences we want students to engage in.” 2 Selecting the most appropriate digital activity will depend on the activity’s level of difficulty tied to the cognitive levels stated within Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy. As K. A. Meyer writes, “Knowledge is situated
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy vs. Digital Bloom’s Taxonomy
Luis
What students are expected to achieve and demonstrate (Based on Bloom’s revised taxonomy) Options for TEL assessment Designing, creating, performing
Pilot Study Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Application for an
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy YouTube
Gabrielle
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Online Resources . A well designed course is built on a foundation of actionable learning objectives. There are numerous lists of action learning verbs. Many of those are based on Bloom’s Taxonomy, which is a classification of actionable objectives for learning opportunities. Bloom’s Taxonomy was published in 1956 under the leadership of educational …
Blooms’ digital taxonomy – 21st century thinking skills
Alyssa
See more What others are saying “The Padagogy Wheel – PADAGOGY 201 It’s a Bloomin’ Better Way to Teach: This seminar gives ideas of the latest use of the Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy and how the iPad can serve the pedagogy.
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy YouTube
David
Blooms Digital Taxonomy Summary Map [Image] (2013) Retrieved June 24. like digital content creation. 2013. This version of the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy is helpful in creating learning opportunities promoting the development of 21st Century skills.Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy A contemporary update to the revised taxonomy is Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy.
Resource Toolkit It Couldn’t Happen To Me
Adrian
REMEMBERINGDEFINITION: (ANDERSON & KRATHWOHL)Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory. Remembering is when memory is used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material.Possible Activities (Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy)Recitation (Word Processing, Mind map, flashcards, presentation tools)Quiz/Test (Online
Integrating Technology with Bloom’s Taxonomy TeachOnline
Bloom’s’Digital’Taxonomy’ The’Swiss’Army’Knife’of’21st
Andrew Churches created Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy
Jose
What students are expected to achieve and demonstrate (Based on Bloom’s revised taxonomy) Options for TEL assessment Designing, creating, performing
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy PDF Montgomery County Public
Elijah
1 Remembering Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Definition (Anderson & Krathwohl) Remembering: Retrieving, recalling or recognising knowledge from memory. Remembering is when memory is used to produce definitions, facts or lists, or recite or retrieve material. Key Verbs (Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy
Bloom’s’Digital’Taxonomy’ The’Swiss’Army’Knife’of’21st
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Ibrahim suliman Academia.edu
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy of Apps & Tools in.pinterest.com
Jesus
The following is a graphical representation of Bloom’s Taxonomy overlaid with cognitive elements as well as methods required for web 2.0 technologies.
Churches A. (2009). Bloom’s digital taxonomy. Educational
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy YouTube
The Technology Driven Student How to Apply Bloom’s
Lillian
1956 Taxonomy. 2001 Taxonomy. 2008 Taxonomy. Defined. The ability to grasp the meaning of material. This may be shown by translating material from one form to another (i.e., words to numbers); by interpreting material (explaining or summarizing); and by estimating future trends (predicting consequences or effects).
Blooms’ digital taxonomy – 21st century thinking skills
William
In my educational experience, I have spent a lot of time in the lower levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy: Remembering, Understanding, & Applying.
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy [PDF Document]
The Technology Driven Student How to Apply Bloom’s
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Ibrahim suliman Academia.edu
Victoria
See more What others are saying “The Padagogy Wheel – PADAGOGY 201 It’s a Bloomin’ Better Way to Teach: This seminar gives ideas of the latest use of the Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy and how the iPad can serve the pedagogy.
Bloom’s Digital Verbs louisville.edu
Gabriel
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Online Resources . A well designed course is built on a foundation of actionable learning objectives. There are numerous lists of action learning verbs. Many of those are based on Bloom’s Taxonomy, which is a classification of actionable objectives for learning opportunities. Bloom’s Taxonomy was published in 1956 under the leadership of educational …
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy vs. Digital Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy PDF Montgomery County Public
Cameron
Andrew has aligned Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy with specific digital skills to create Bloom’s Digital taxonomy. The image below is a re-drawing of Andrew’s original diagram . (Click on the image for a pdf …
(PDF) Bloom’s digital taxonomy setting new objectives and
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Verbs Instructional Design
Mason
What students are expected to achieve and demonstrate (Based on Bloom’s revised taxonomy) Options for TEL assessment Designing, creating, performing
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy iTeach Blooms taxonomy
Blooms Digital Taxonomy QuickSheets [PDF Document]
Resource Toolkit It Couldn’t Happen To Me
Logan
What students are expected to achieve and demonstrate (Based on Bloom’s revised taxonomy) Options for TEL assessment Designing, creating, performing
Blooms Digital Taxonomy QuickSheets [PDF Document]
Integrating Technology with Bloom’s Taxonomy TeachOnline
Global Digital Citizen Foundation| Bloom’s Digital
Gabriella
Blooms Digital Taxonomy Summary Map [Image] (2013) Retrieved June 24. like digital content creation. 2013. This version of the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy is helpful in creating learning opportunities promoting the development of 21st Century skills.Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy A contemporary update to the revised taxonomy is Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy.
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy PDF Montgomery County Public
Andrew Churches Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy.pdf Ferry
Global Digital Citizen Foundation| Bloom’s Digital
Brandon
But, please keep in mind that many tools/apps can easily be used for all the levels of Bloom’s taxonomy with an open and creative mindset. Therefore, don’t be fooled by these Bloom’s digital taxonomies shared below, and use them instead to discover new tools and ways to inspire more engaging and creative learning.
Blooms Taxonomy Learning Pedagogy
The Technology Driven Student How to Apply Bloom’s
Bloom’s’Digital’Taxonomy’ The’Swiss’Army’Knife’of’21st
Charles
A New Wonderful Wheel on SAMR and Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy ~ Educational Technology and Mobile Learning. This a great quick chart that is color coded and with pictures of the apps that apply to each level of SAMR and Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy models.
Global Digital Citizen Foundation| Bloom’s Digital
Articles by Andrew Churches Tech & Learning
Blooms Digital Taxonomy QuickSheets [PDF Document]
Jordan
A New Wonderful Wheel on SAMR and Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy ~ Educational Technology and Mobile Learning. This a great quick chart that is color coded and with pictures of the apps that apply to each level of SAMR and Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy models.
Promoting Student Learning Outcomes with Bloom’s Revised
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy YouTube
Brian
Bloom’s Original Taxonomy to Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy to the start of what is termed Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy. The authors argue that current restrictions on the use of technology in the classroom, although well
Bloom's Taxonomy Blooms Digitally Tech & Learning
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy iTeach Blooms taxonomy
Lucas
The below overview shows the progression of Bloom’s Taxonomy, how each thinking skill applies in practice, and examples of activities using digital tools. Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Bloom’s’Digital’Taxonomy’ The’Swiss’Army’Knife’of’21st
bloom’s digital taxonomy understanding – Dartmouth College
Maria
The original Blooms taxonomy has been revised and an additional Digital taxonomy has been developed to accommodate for the integration of technology in today’s 21st Century classrooms (F2F and
Blooms Digital Taxonomy QuickSheets [PDF Document]
How are faculty using the Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy in
Bloom’s taxonomy dft.westernsydney.edu.au
Taylor
1956 Taxonomy. 2001 Taxonomy. 2008 Taxonomy. Defined. The ability to grasp the meaning of material. This may be shown by translating material from one form to another (i.e., words to numbers); by interpreting material (explaining or summarizing); and by estimating future trends (predicting consequences or effects).
Blooms Digital Taxonomy v2.12 Web Search Engine Tag
Kayla
Andrew has aligned Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy with specific digital skills to create Bloom’s Digital taxonomy. The image below is a re-drawing of Andrew’s original diagram . (Click on the image for a pdf …
Bloom’s Digital Verbs louisville.edu
Blooms’ digital taxonomy – 21st century thinking skills
Blooms Taxonomy Learning Pedagogy